blue
Lesson 1: Git
Git Overview
What is Git?
- Git is a software for tracking changes in files.
- Programmers use git to track changes made to code.
- Git synchronizes code between different people.
What is GitHub?
- GitHub is a user interface, or UI, wrapper around Git, much like Spotify is a UI wrapper around music. In these cases, a core technology (Git; music) is wrapped in a graphical user interface (GitHub; Spotify).
- Sites like GitHub host Git repositories, or file systems that are tracked by Git.
Why do we need Git?
- Using Git allows you to save your code online. This means if you ever lose your local files (eg: laptop gets stolen), you still have a copy of your code through Git.
- Git also allows collaborators to concurrently work on the same project, sort of like how Google Docs allows users to edit the same text document online.
- Finally, Git allows you to save “states” of your code, which allows you to revert to a previous state at any point in time.
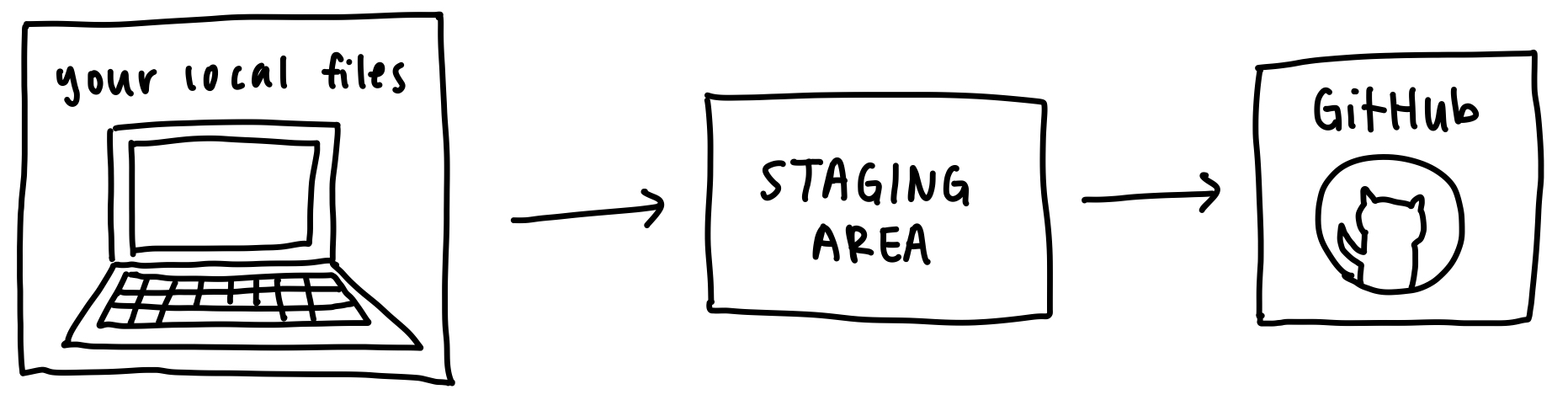
Git Workflow
Git Basics
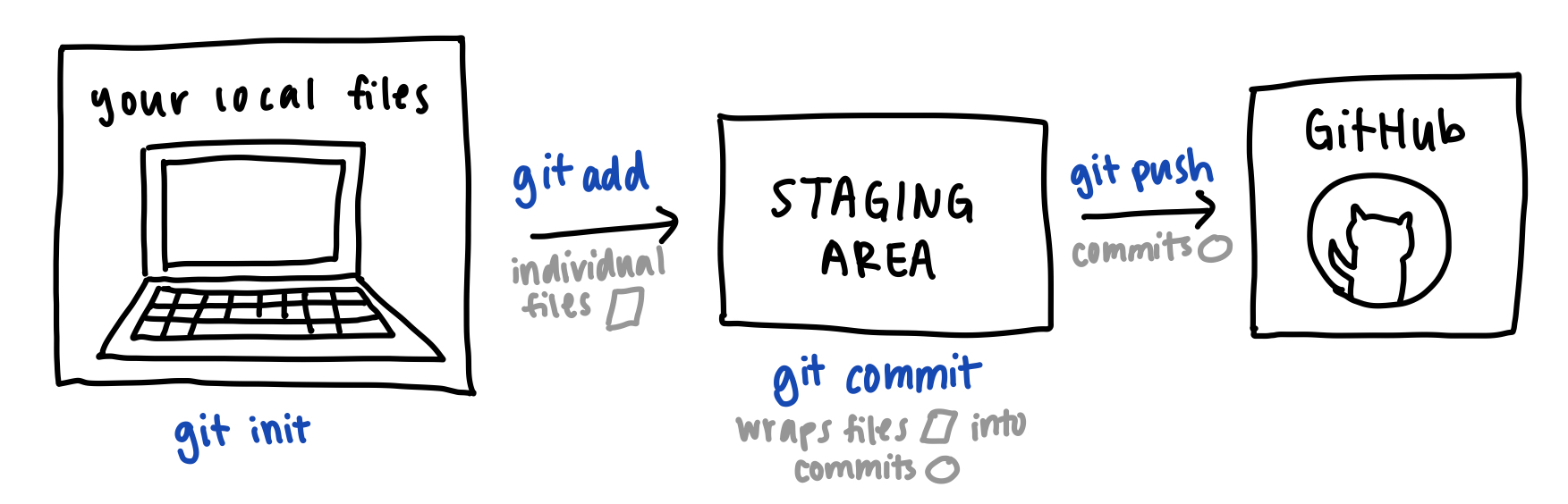
Git Setup
git init: Initializes git within a local directory.git remote add origin REPO_PATH: Sets origin of git to repository atREPO_PATH(eg: repo path could be https://github.com/PennSpark/blue.git)git status: Check the status of files tracked by Git
Git Workflow
git add FILENAME: Adds the fileFILENAMEto the staging area.git commit -m "message here": Prepares everything in the staging area into a single “commit”, which you can think of as a wrapper that contains all the changes made to your local files as well as storing metadata such as commit message.git push: Pushes all the commits in the staging area to GitHub!
Spark Resources
- Git Slides
- Git Workshop Activity (written by Akshay S.)
- Git Setup Guide (written by Akshay S.)
- Lesson Recording (Spark members only)
- Git Deliverable
Written by Grace J.